By Anthony Quirk
|
Friday 4th November 2005 |
Text too small? |
|
This market summary is provided by Tyndall Investment Management New Zealand Limited (Tyndall). To see how the numbers stacked up for various markets around the world in the past month and over the year, visit our Monthly Market Review here |
A look back at history
For most developed countries the October 1987 crash was a mere blip, with sharemarkets on a relentless path upwards through the late 1980s and 1990s, culminating in the tech bubble, which crashed so spectacularly.
In the US in late 1987 there was very real concern that the post-1929 crash situation could be repeated, when authorities did tighten policy settings leading to the great Depression of the early 1930s. So the US Federal Reserve injected liquidity into the system after the '87 crash and any significant fall out was averted.
New Zealand was a contrast to this with little attempt to "massage" the markets through a tough period. Short-term interest rates remained in the mid-double digits for an extended period after the '87 crash.
While New Zealand did not have anything like the great Depression in the aftermath of the '87 crash, high interest rates and falling investor confidence certainly had an impact! The froth and bubble of "paper shuffling" listed investment companies was decimated, as were many investors' savings. Listed property companies were also hard hit with most companies in that sector collapsing by the early 1990s.
Thus the pre-crash excesses in New Zealand financial markets were eventually removed. In its place emerged a much stronger listed corporate sector populated by companies that actually added real value and which had sound management, balance sheets and earnings profiles. In other words the short-term pain eventually led to long-term gain for the country's financial markets.
A guide to the future?
Moving ahead to the present, there seem to be some parallels here. The current RBNZ Governor is clearly very concerned about the excesses and imbalances within the New Zealand economy at present. These include the reliance of the economy on buoyant residential property prices and the consumer borrowing and spending binge that has followed. This, in turn, has been a contributor to rising inflationary pressures and to our alarming current account deficit, which is now at 8% of GDP – the worst in over 20 years.
The RBNZ is currently taking a hawkish stance to try to eliminate investment and borrowing excesses. In doing so they run the risk of a significant correction in the economy and markets as a material adjustment occurs – as we saw in the five years following the 1987 crash.
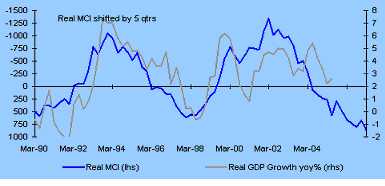
The impact of high interest rates and currency on GDP and the sharemarket
The extent of the current tightening cycle is shown in the following graph. This shows the effect of the mixture of interest rates and high exchange rates – the so called "MCI" measure. It confirms that the current policy mix is the tightest it has been for the past ten years.
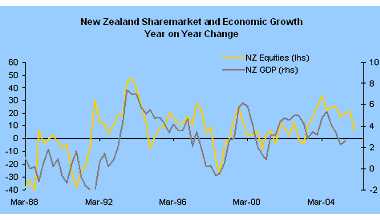
I think we have another parallel here with the strong residential property market having a widespread positive influence on the general economy and on many listed companies. The most obvious sector to currently benefit from this is the financial sector, with many finance companies heavily exposed to loans related to the property sector. A significant property downturn may cause problems for some finance companies with potential ramifications for depositors with those companies, as well as second and third round casualties. While we are not in a "bubble" economy quite like 1987 there are some elements that are vulnerable to the currently very tight settings.
The good news – fiscally we are in great shape
So we are in a Mexican stand off at present with the RBNZ Governor trying to talk down the housing market. However, he seems quite prepared to back this up with action and therefore the New Zealand economy and sharemarkets may be in for a rough ride!
To see how the numbers stacked up for various markets around the world in the past month and over the year, visit our Anthony Quirk is the managing director of Tyndall Investment Management New Zealand Limited (Tyndall). No comments yet
MARKET CLOSE: Telecom and Air New Zealand gain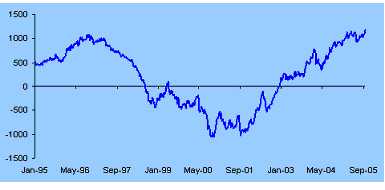
Source: First NZ Capital
Source: First NZ Capital
Source: First NZ Capital
The silver lining on this cloud is the excellent fiscal position we are in currently (in contrast to the late 1980s). This does give the Government some latitude to "manage" any economic downturn. However, the buoyant residential sector is also helping boost the Government's coffers and while the cupboard may not be bare, current fiscal surplus levels may diminish as the economy (and the housing sector) turns down.

Comments from our readers
Add your comment:
Related News:
MARKET CLOSE: NZX 50 snaps 4-day slide as earnings awaited; Mainfreight gains
MARKET CLOSE: Auckland Airport feels effects of global downturn
MARKET CLOSE: Shares fall with global slide; Rakon, Nuplex fall
MARKET CLOSE: Pumpkin Patch slips as investors mull downsizing
MARKET CLOSE: Weaker building stats weigh on Fletcher Building
MARKET CLOSE: Telecom and Contact Energy make gains
MARKET CLOSE: NZ shares mixed, FPA, Sky City fall, Rakon gains
MARKET CLOSE: NZ shares gain; Telecom lifts on Chorus, Sky City gains
MARKET CLOSE: NZ shares fall a second day; Wrightson drops on forecast